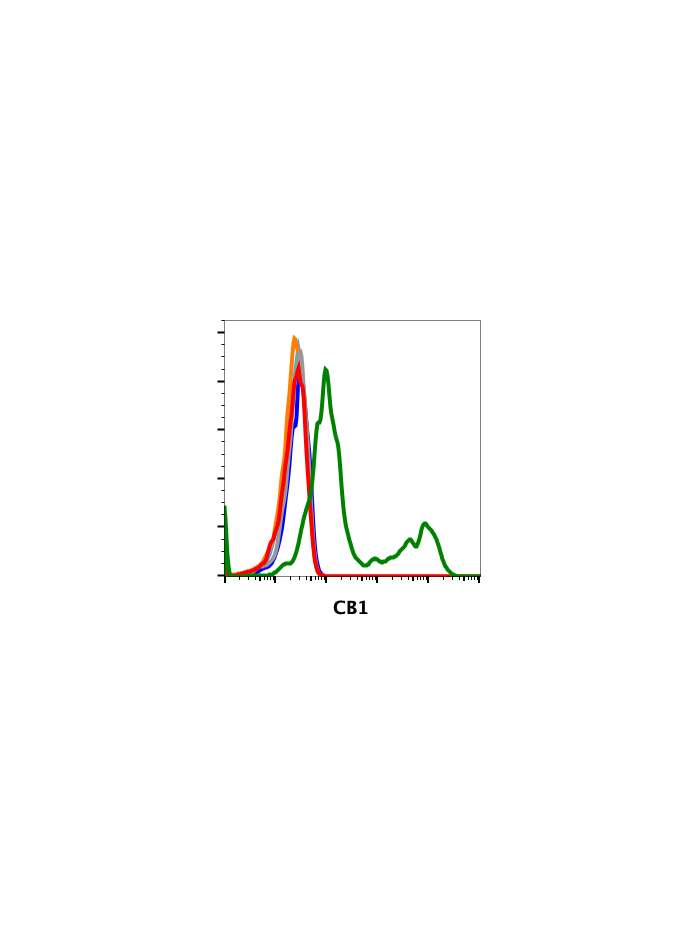
Cannabinoid Receptor (CB1) (H6) rabbit mAb
The CB1 cannabinoid receptor was discovered in 1988 (1) and subsequently cloned (2) on the basis of its responsiveness to (−)-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC). Δ9-THC is the primary psychoactive constituent in Cannabis (marijuana), hence the name “cannabinoid” receptor was coined. CB1 is a member of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) family. An arachidonic acid metabolite, N-arachidonylethanolamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) was found to activated CB1 receptor (3). The second cannabinoid receptor (CB2) was isolated from differentiated myeloid cells. The CB2 receptor shares 44% amino acid homology with CB1, and a distinct yet similar binding profile, thus representing a receptor subtype.
The CB1 receptor is one of the most abundant GPCRs in the brain; it is highly expressed in the basal ganglia nuclei, hippocampus, cortex and cerebellum (5,6). The CB1 distribution within the central nervous system correlates with its role in the control of motor function, cognition and memory, and analgesia. CB1 receptors are primarily localized to the terminals of central and peripheral neurons, where they mediate inhibition of neurotransmitter release (7). CB1 receptors are found in higher levels on GABAergic than glutamatergic neurons in various brain regions. CB1 receptors are also present on astrocytes, where they are expressed at much lower levels than on neurons; but where they have been shown to modulate synaptic transmission and plasticity (8,9). The CB2 receptor is expressed in peripheral organs with immune function, including macrophages, spleen, tonsils, thymus, and leukocytes, as well as the lung and testes (10). Initial studies suggested that CB2 receptors were absent from the healthy brain (11).
| Applications | Flow Cytometry |
|---|---|
| Clone | CB1-H6 |
| Format | Unconjugated |
| Validated Reactivity | Human |
| Cross Reactivity | Predicted to work with mouse, rat and other homologues. |
| Detection | Anti-Rabbit IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | Synthetic peptide |
| Formulation | 1X PBS, 0.025% NaN3, 0.2% BSA |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgGk |
| Preparation | Protein A+G |
| Recommended Usage | For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells or 5 µL per 100 µL of staining volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application. See product image legends for additional information. |
| Storage | -20ºC |
| Pseudonyms | Cannabinoid receptor 1, CB1 receptor |
| Uniprot ID | P21554 |
| References | 1. Devane WA, et a., 1988, Mol Pharmacol, 34:605-613. 2. Matsuda LA, et at al., 1990, Nature, 346:561-564. 3. Mechoulam R, et al., 1995, Biochem Pharmacol, 50:83-90. 4. Munro S, et al., 1993 Nature, 365:61-65. 5. Glass M, et al., 1997, Neuroscience, 77:299-318. 6. Herkenham M, et al., 1990, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 87:1932-1936. 7. Szabo B, and Schlicker E, 2005, Handb Exp Pharmacol, 168:327-365. 8. Han J, et al., 2012, Cell,148:1039-1050. 9. Oliveira da Cruz JF, et al., 2016, Neuroscience, 323:35-42. 10. Brown SM, et al., 2002, Biochim Biophys Acta, 1576:255-264. 11. Galiègue S, et al., 1995, Eur J Biochem, 232:54-61. |