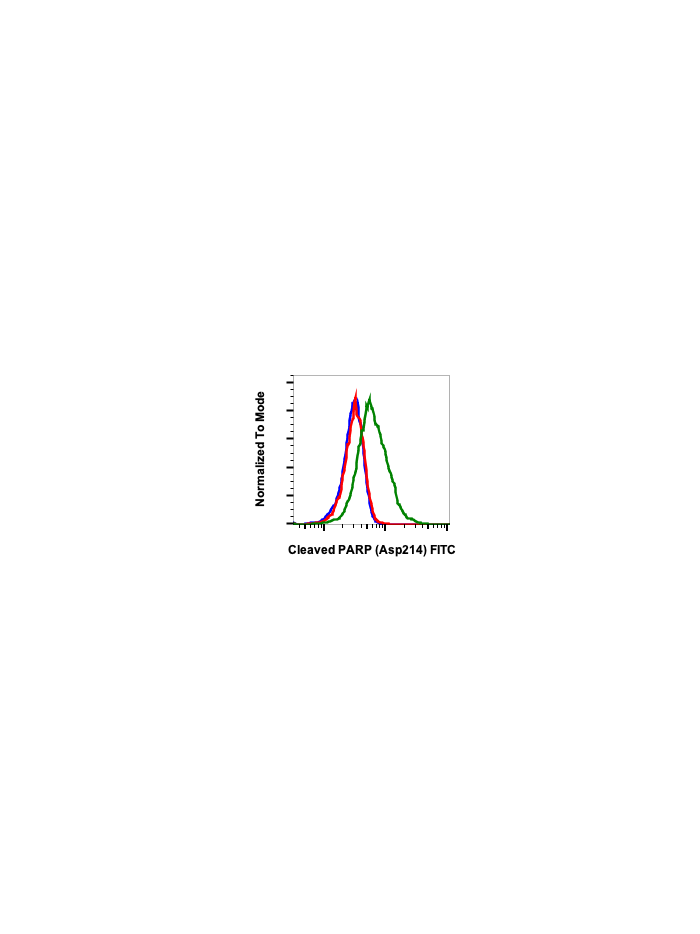
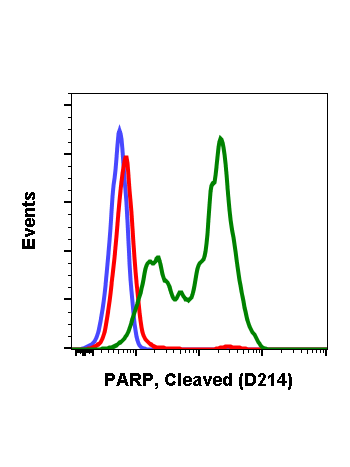
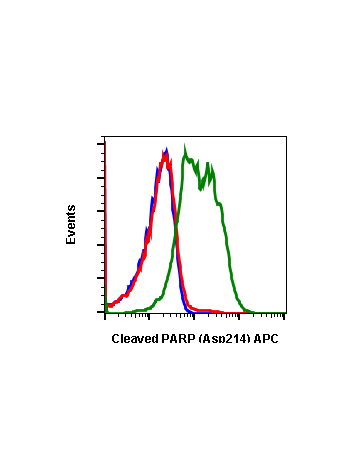
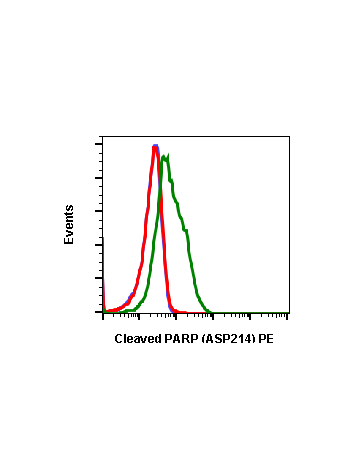
Cleaved PARP (Asp214) (H8) rabbit mAb FITC conjugate
From
$118.80
In stock
Only %1 left
SKU
2333
Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase 1 (PARP-1), is a substrate of caspase-3 and caspase-7, both of which play a dominant role in apoptosis. PARP is cleaved into 89 and 24 kDa fragments at Asp214. The detection of these fragments is used as an indicator of caspase activation and apoptosis induction for many cell lines. Under normal conditions, PARP aids in the detection and repair of DNA damage. With 1-2 million copies per nucleus, PARP is also involved in poly (ADP-ribosyl)ation, a post-translational protein modification mechanism used to modify chromatin structure and regulate transcription. Decreased PARP activity has been shown to lead to loss of memory and neuronal cell death.
| Applications | Flow Cytometry |
|---|---|
| Clone | PARP-H8 |
| Format | FITC |
| Validated Reactivity | Human |
| Cross Reactivity | Predicted to work with mouse, rat and other homologues. |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to residues surrounding Asp214 of human PARP |
| Formulation | 1X PBS, 0.09% NaN3, 0.2% BSA |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgGk |
| Preparation | Protein A+G |
| Recommended Usage | For flow cytometric staining, the suggested use of this reagent is 5 µL per million cells or 5 µL per 100 µL of staining volume. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application. See product image legends for additional information. |
| Storage | 2-8ºC |
| Pseudonyms | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1, PARP-1, ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 1, ARTD1, NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 1, ADPRT 1 |
| Uniprot ID | P09874 |
| References | Bressenot A, Marchal S, Bezdetnaya L, Garrier J, Guillemin F, and Plenat F. (2009) Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 57: 289-300. Chaitanya GV, Alexander JS, and Babu, PP. (2010) Cell Communication and Signaling. 8:31. Kraus WL, and Lis JT. (2003) Cell. 113:677-683. |
Write Your Own Review