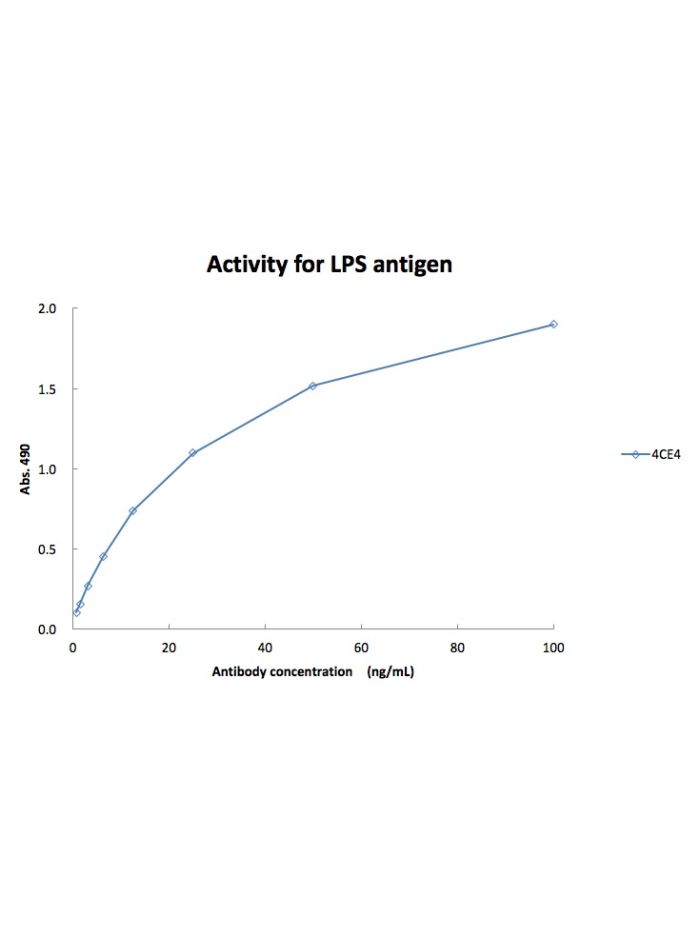
Legionella pneumophila LPS (serogroup 1) mouse mAb
From
$90.00
In stock
Only %1 left
SKU
2026
Legionella pneumonia, first discovered after an outbreak in Pennsylvania in 1976 at the American Legion convention, is a common cause of community-acquired pneumonia. Legionella are gram-negative bacteria found in natural aquatic environments, where they are intracellular parasites of protozoa. The serogroup 1 strains most commonly cause human infections. Serotyping can be performed by antibody subgrouping, pulsed-field gele electrophoresis, or DNA sequencing. The lipopolysaccharide, LPS or endotoxin, of serogroup 1 is a bacterial virulence factor that contains 10-75 residues of the unique sugar termed legionaminic acid. Lacking free hydroxyl groups renders this LPS hydrophobic, allowing the bacterium to adhere to target cell membranes including macrophages in the lung.
| Applications | ELISA |
|---|---|
| Clone | AWB4CE4 |
| Format | Unconjugated |
| Validated Reactivity | Other |
| Cross Reactivity | No known reactivity to other Legionella pneumophila serogroups |
| Detection | Anti-Mouse IgG |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Immunogen | LPS conjugated to BSA |
| Formulation | 1X PBS, 0.02% NaN3, 50% Glycerol, 0.1% BSA |
| Isotype | Mouse IgGk |
| Preparation | Protein A+G |
| Recommended Usage | 1µg/mL – 0.001µg/mL. It is recommended that the reagent be titrated for optimal performance for each application. See product image legends for additional information. |
| Storage | -20ºC |
| References | Ratzow S, Gaia V, Helbig JH, Fry NK, and Luck PC. (2007) Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 45: 1965-1968. Zahringer U, Kinirel YA, Linder B, et al. (1995) Progress in Clinical Biological Research. 392: 113-139. |
Write Your Own Review